
1.6 Transformers
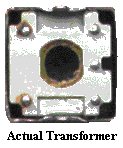
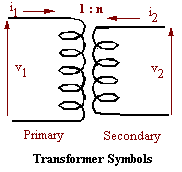 In its simplest form a transformer may be used to convert the fluctuating
voltage and current of an electrical supply. Physically, a transformer consists
of an iron core around which are wound two wire coils, the primary and
secondary. The currents flowing in the coils are linked by the electromagnetic
field produced in the core. Their relationship depends on the relative number of
turns in each coil. If n is the ratio
of the number of turns in the secondary to that in primary then
the currents in the primary and secondary, i1 and i2 are related by the equation
In its simplest form a transformer may be used to convert the fluctuating
voltage and current of an electrical supply. Physically, a transformer consists
of an iron core around which are wound two wire coils, the primary and
secondary. The currents flowing in the coils are linked by the electromagnetic
field produced in the core. Their relationship depends on the relative number of
turns in each coil. If n is the ratio
of the number of turns in the secondary to that in primary then
the currents in the primary and secondary, i1 and i2 are related by the equation
i2 = i1 / n The voltages are similarly related
v2 = n v1 The iron core is a crucial part of this device. Removing it reduces
the magnetic coupling almost to zero.

 In its simplest form a transformer may be used to convert the fluctuating
voltage and current of an electrical supply. Physically, a transformer consists
of an iron core around which are wound two wire coils, the primary and
secondary. The currents flowing in the coils are linked by the electromagnetic
field produced in the core. Their relationship depends on the relative number of
turns in each coil. If n is the ratio
of the number of turns in the secondary to that in primary then
the currents in the primary and secondary, i1 and i2 are related by the equation
In its simplest form a transformer may be used to convert the fluctuating
voltage and current of an electrical supply. Physically, a transformer consists
of an iron core around which are wound two wire coils, the primary and
secondary. The currents flowing in the coils are linked by the electromagnetic
field produced in the core. Their relationship depends on the relative number of
turns in each coil. If n is the ratio
of the number of turns in the secondary to that in primary then
the currents in the primary and secondary, i1 and i2 are related by the equation