
2.3 Two Devices Connected
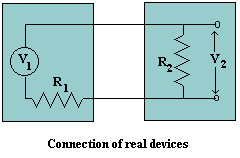 Now consider a common situation in which the output of
one device is connected to the input of another. The
relationship between the voltages v1
and v2 in this situation
is obtained simply by applying Ohm's law. We see that
i = v1 / ( R1 + R2 ) =
v2 / R2 and thus,
Now consider a common situation in which the output of
one device is connected to the input of another. The
relationship between the voltages v1
and v2 in this situation
is obtained simply by applying Ohm's law. We see that
i = v1 / ( R1 + R2 ) =
v2 / R2 and thus,
v2 / v1 = R2 /
( R1 + R2 ) Ideally we want the voltage signal to be transferred unaltered
between the two devices, i.e. we want, as near as possible v1 = v2. To obtain this the
input resistance of the second device (R2) must
clearly be much greater than the output resistance of the first
(R1). Note that this is not the only possible
desirable outcome. We may wish instead for maximum possible
electrical power to be transferred between the two devices.
It is simple matter to show that this occurs when R1 = R2.
 Now consider a common situation in which the output of
one device is connected to the input of another. The
relationship between the voltages v1
and v2 in this situation
is obtained simply by applying Ohm's law. We see that
Now consider a common situation in which the output of
one device is connected to the input of another. The
relationship between the voltages v1
and v2 in this situation
is obtained simply by applying Ohm's law. We see that